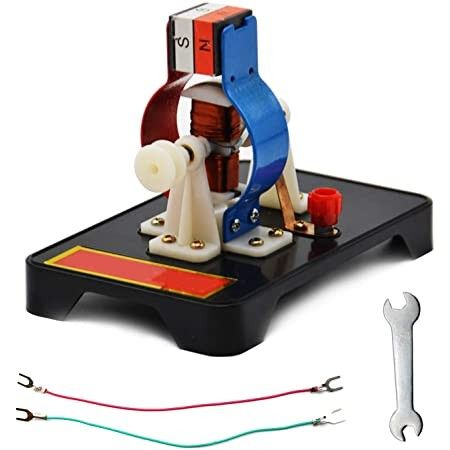

DC Electric Motor
The DC electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. An electric current flows through a coil which is subject to a magnetic field. As a consequence a force is generated which is perpendicular to both the coil and magnetic field generating a rotational movement. As the strength of a current increases so does the strength of the magnetic field.
DC brush motors use contact brushes that link to a commutator to invert the current direction. These motors are inexpensive and simple to control. The major drawback is its reduced lifetime as brushes wear out. Brush heating and electromagnetic noise are other downsides.
Current:
Too much current will damage the motor. The average current the motor draws under typical torque is called operating current. The maximum current the motor can take is called stall current. This is typically the current necessary to make the motor run from stall speed (0 RPM). Heat sinks are important to dissipate the heat and keep the motor temperature under operating limits which otherwise would cause permanent damage (melting coils).
Voltage:
The higher the voltage, the higher the torque. The nominal voltage is the typical value the motor should be running at. This is important to maximise the efficiency of the motor. A lower voltage won’t be enough to move the motor. A very high voltage could cause short windings and loss of power.
Torque:
The torque or moment of a force (T = F x d) is the tendency of a force to rotate the body to which it is applied. Operating torque is the nominal torque the motor was designed for. Stall torque is the amount of torque required to produce motion from a stalled state.
Velocity:
Velocity is usually measured in rotations per minute (RPM). DC motors are more efficient at high speed but really depends how much gearing is required. Gears reduce the efficiency of the motor, so it’s important to design/choose a motor taking into account speed and torque reduction all together.
Components:
- DC power supply
- Pair of brushes
- Coil to generate magnetic field
- Commutator to reverse current
Working Principle:
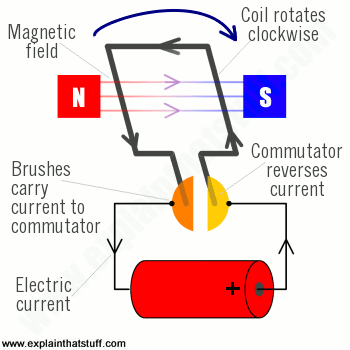
A machine that converts DC electrical power into mechanical power is known as a Direct Current motor.
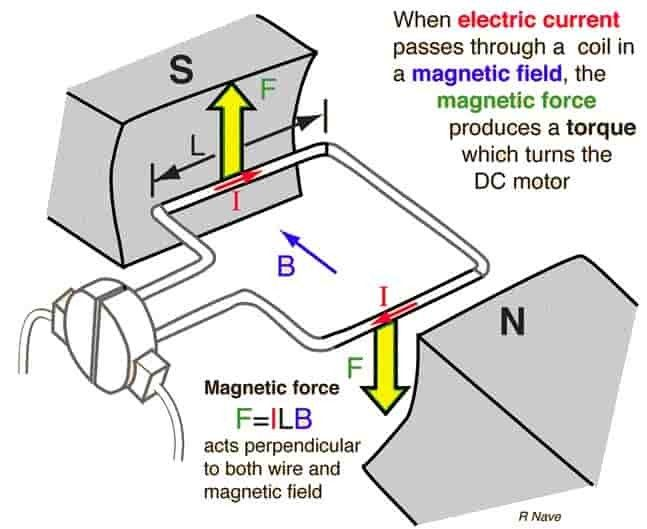
DC motor working is based on the principle that when a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, the conductor experiences a mechanical force.
The direction of this force is given by Fleming’s left-hand rule and magnitude is given by;
F = BIL Newtons
According to Fleming’s left-hand rule when an electric current passes through a coil in a magnetic field, the magnetic force produces a torque that turns the DC motor.
The direction of this force is perpendicular to both the wire and the magnetic field.
Basically, there is no constructional difference between a DC motor and a DC generator. The same DC machine can be run as a generator or motor.
Instructions:
Power the circuit and watch the motor spinning. You can add a pulley to the shaft to action another mechanical component (e.g. wheel).
Links:
Working Principle of DC Motor (animation of elementary model)
How motors work and how to choose the right motor for any project