
Gearbox kit
A gearbox is a collection of gears of various sizes. The number of gears in the gearbox provides the perfect combination of traction and speed. With short gearing, you get better acceleration or pick-up, while tall gearing gives you higher top speed. A vehicle that is climbing a slope requires more torque than one that is travelling down a straight road.
A gearbox is a metal container that houses a collection of gears, synchronising sleeves, and a gear-shifting mechanism. All of the gears are housed in the metal housing, which is commonly composed of aluminum/iron casting. Because the gears play a vital role in conveying engine power to the wheels, the gearbox is considered part of the ‘transmission’ system.
Components:
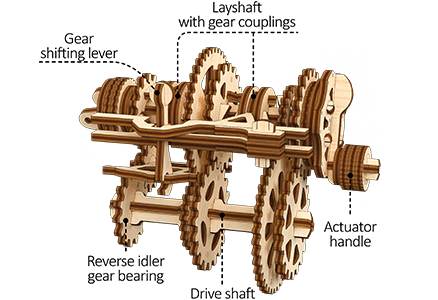
- Gear shifting lever
- Layshaft with gear couplings
- Reverse idle gear bearing
- Drive shaft
- Actuator handle
Working Principle:
The first gear in a gearbox is the largest and produces the most torque while producing the least speed.
As a result, it is utilised to ascend slopes.
Between 1st and last gear, the size of each gear decreases in a decreasing ratio.
As a result, it offers a diverse range of pulling ability and speed.
As a result, the car may be driven smoothly without experiencing any acceleration drops.
In essence, the gearbox increases the vehicle’s driveability in all conditions.
The ratio between the input and output gears is known as the gear ratio.
Gear Ratio = No. of teeth of output gear / no. of teeth of the input gear
e.g. if no. of gears on input (driving) gear = 30 and no. of gears on output (driven) gear = 105
then, the Gear ratio = 105/30 = 3.5 : 1 because to rotate the output (driven) gear by 1 rotation, you need to turn the input (driving) gear by 3.5 rotations.
The gear ratios differ from one vehicle to the next.
Trucks have larger gear ratios than cars because they have to carry a heavier load.
When driving a car, you must have both speed and traction.
Depending on the driving conditions, the gears in the gearbox assist you in selecting one of them.
Lower gears, such as 2nd and 1st, provide the most traction, whereas higher gears, such as 5th and 6th (if available), provide the fastest speed.
Inventor
Karl Benz, a well-known German engineer, is credited with developing the gearbox.
Instructions:
- Select Position “N” – idle in which both clutch gears of layshaft remain uncoupled and idling; Rotate the actuator handle clock-wise and verify that the output remains idle.
- Select the first gear and check that the output gear rotates with the lowest speed;
- Select the second gear and verify that the drive shaft along with the flywheel rotates with an average speed.
- Select the third gear that allows the layshaft and all gears rotate with the highest speed.
- Switch on the reverse gear by moving the clutch gear to the left towards gear “R”and all gears will rotate in reverse.
Links:
«Gearbox» educational mechanical model kit
Manual Transmission, How it works?
How Gearbox | Manual Transmission Works
How A Gear box (Transmission) works? What’s Gear Ratio?
A Gearbox Specialist’s Guide to How a Gearbox Works